In under a year, the AI agent landscape has grown from roughly 300 players to thousands. Agents are making their way into workflows across verticals, from e-commerce to industrials.
Underpinning this momentum is an emerging tech stack. Infrastructure layers — from foundation models to oversight — are helping enterprises build, deploy, and manage AI agents more effectively.
Using the CB Insights Business Graph and proprietary signals, we mapped 135+ promising private companies building infrastructure for AI agents.
Below the map, we outline the emerging markets and trends investors and strategy leaders should be watching.
![]() Track 250+ companies building AI agent infrastructure
Track 250+ companies building AI agent infrastructure
We selected companies for inclusion based on Mosaic health scores (500+) and funding recency (since 2023). Includes private companies only, organized according to their primary focus. Excludes general enterprise workflow automation platforms and non-pure-play LLM developers. This market map is not exhaustive of the space.
Please click to enlarge.
Private market momentum points to payments, voice, and security as key markets to watch
The AI agent tech stack is a high-momentum landscape, based on CB Insights Mosaic startup health scores. Private companies across the markets outlined below have an average Mosaic score of 768 — more than double the average of 370 for all private companies. They also have an average Commercial Maturity Score of 3, indicating widespread solution deployment.
A deeper dive into these scores, partnerships, and funding reveals 3 emerging markets to watch:
Voice AI is the new battleground for the next wave of AI agents: With an average Mosaic score of 756 and nearly $400M in funding in 2025 so far, voice AI development platforms are building momentum. Big tech also recognizes voice as an essential AI building block — Meta’s first acquisitions since 2022 this year were PlayAI and WaveForms AI, both operating in audio and voice AI.
AI agent security startups see rapid momentum growth: AI agents create new attack surfaces and data breach risks, driving urgency for agent security startups. Companies in the market averaged a 56-point Mosaic score growth over 12 months, with Zenity, WitnessAI, and TrojAI each gaining 100+ points. The companies with the highest jumps in Mosaic score are partnering with larger tech firms and cybersecurity leaders. Public and established companies have also entered the conversation, with identity leader Okta and cybersecurity giant Palo Alto Networks both building agent security into their platforms.
AI agent payments startups get backing from incumbents: Agent payments infrastructure is one of the more nascent markets in this tech stack, with an average Commercial Maturity of 2.4 (validating) and an average Mosaic score of 697. The barrier to entry in payments is high, requiring complex technical and regulatory infrastructure. In an indication of the tech’s potential, established card and payment networks are investing and partnering with startups in the market: Coinbase backed Skyfire and Catena, Visa invested in Payman, and American Express participated in Nekuda’s recent seed round. Others like Crossmint and pre-funding PayOS have partnered with Visa and Mastercard.
Major LLM providers and tech incumbents all try to own a piece of the open standards pie
The growth of AI agents and development platforms has created a need to facilitate communication between agents and access to context. LLM developers and major tech companies are competing to own these standards.
In less than a year:
Anthropic launched Model Context Protocol (MCP), standardizing how AI agents connect to external tools and data sources
Google created the Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol that allows agents to collaborate with each other, regardless of underlying framework
IBM introduced Agent Communication Protocol, which enables inter-agent communication across technologies and systems within a local environment
These protocols have quickly become table stakes across the AI agent value chain. Professional services firms like Accenture, McKinsey, Deloitte, and KPMG contributed to Google’s A2A, and big tech companies like Microsoft and AWS support MCP. Meanwhile, startups in the tool libraries & integrations platform market like Speakeasy and Stainless are helping companies build MCP-compatible interfaces for their APIs (known as MCP servers), enabling AI agents to interact with their services.
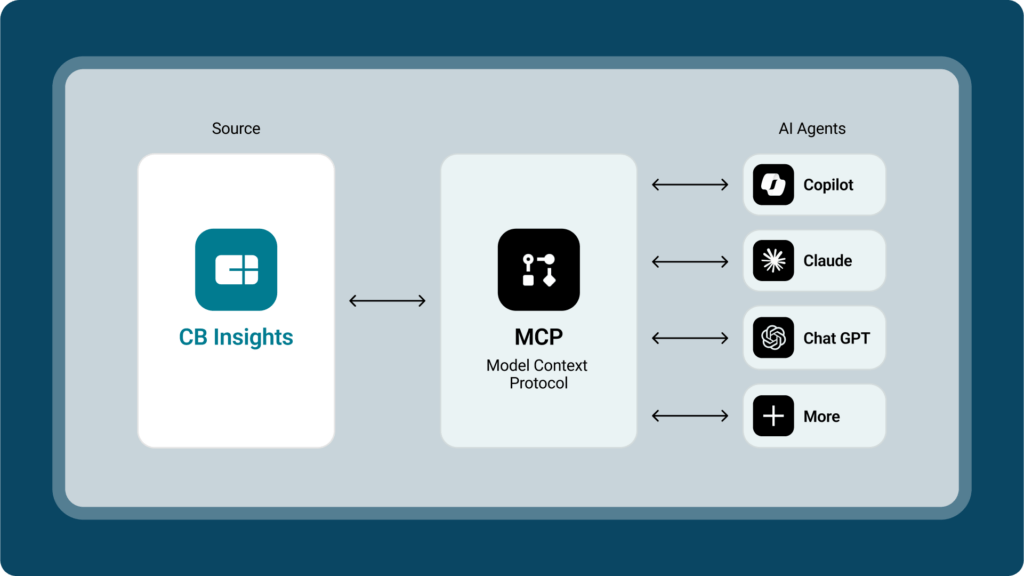
MCP for the win: Make your AI smarter with our data and tools
Any MCP-compatible AI agent can tap into CB Insights’ datasets and tools – including ChatCBI – without a single line of code. Install our server into your environment to get started. Learn more here.
Big tech pushes deeper into AI agent development
While the above market map highlights the private landscape, tech giants and incumbents are also active across the AI agent infrastructure landscape. The top 3 global cloud providers — Amazon, Microsoft, and Google — are expanding their AI agent offerings across development tooling, hosting, orchestration, and more.
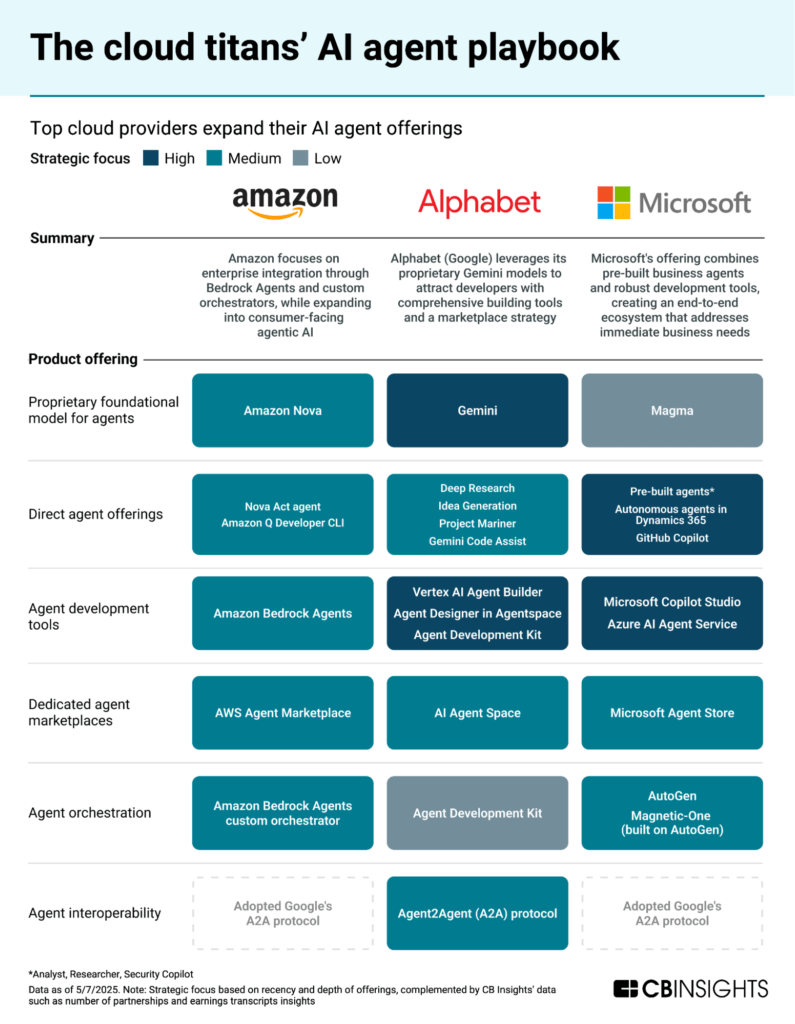
Dive into the full report on how cloud leaders are shaping AI’s next frontier here.
With many enterprises favoring established vendors, big tech companies have significant advantages in AI agent development. Similarly, enterprise software incumbents like Salesforce (Agentforce) and ServiceNow (AI Agent Marketplace) have launched agent platforms and marketplaces targeting their installed bases.
Yet startups across the stack are carving out defensible positions by solving specific technical challenges and pushing the boundaries of what agents can do across areas like multi-agent orchestration (CrewAI) and enterprise data preparation (LlamaIndex). In the crowded AI agent development market, end-to-end platforms like WRITER and Dust are differentiating with vertical-specific implementations and promising speedy deployments.
Autonomous agents drive the need for an oversight layer
AI agent reliability remains a major challenge in the landscape. Agents that fail, hallucinate, or behave unpredictably create immediate business risk.
This is driving activity across observability, evaluation, and governance applications. The market has already seen 2 acquisitions in 2025 YTD. Early-stage activity highlights emerging technical needs, such as voice agent testing, with both Cekura ($2.4M seed) and Coval ($3.3M seed) focusing on evaluating and monitoring voice AI agents via simulated conversations.
Securing agents is a growing priority across the stack. Based on one-year funding activity, the AI agent security & risk management market is the fastest-growing cybersecurity segment we track as agents proliferate across enterprise environments.
White space opportunities for the AI agent ecosystem
As the AI agent tech stack matures, we predict the following areas will attract increasing innovation based on early-stage activity and recent product launches:
AI agent marketplaces: Distribution is a competitive advantage, with all major cloud providers launching dedicated AI agent marketplaces, including AWS in July 2025. Companies like Olas and Agent.ai are looking to differentiate through specialized agent discovery and customization.
AI agent monetization: Monetization emerges as an untapped opportunity, with companies like Paid giving visibility into AI agent costs and profit opportunities, and AGI Open Network tokenizes AI agents as tradable assets on blockchain networks.
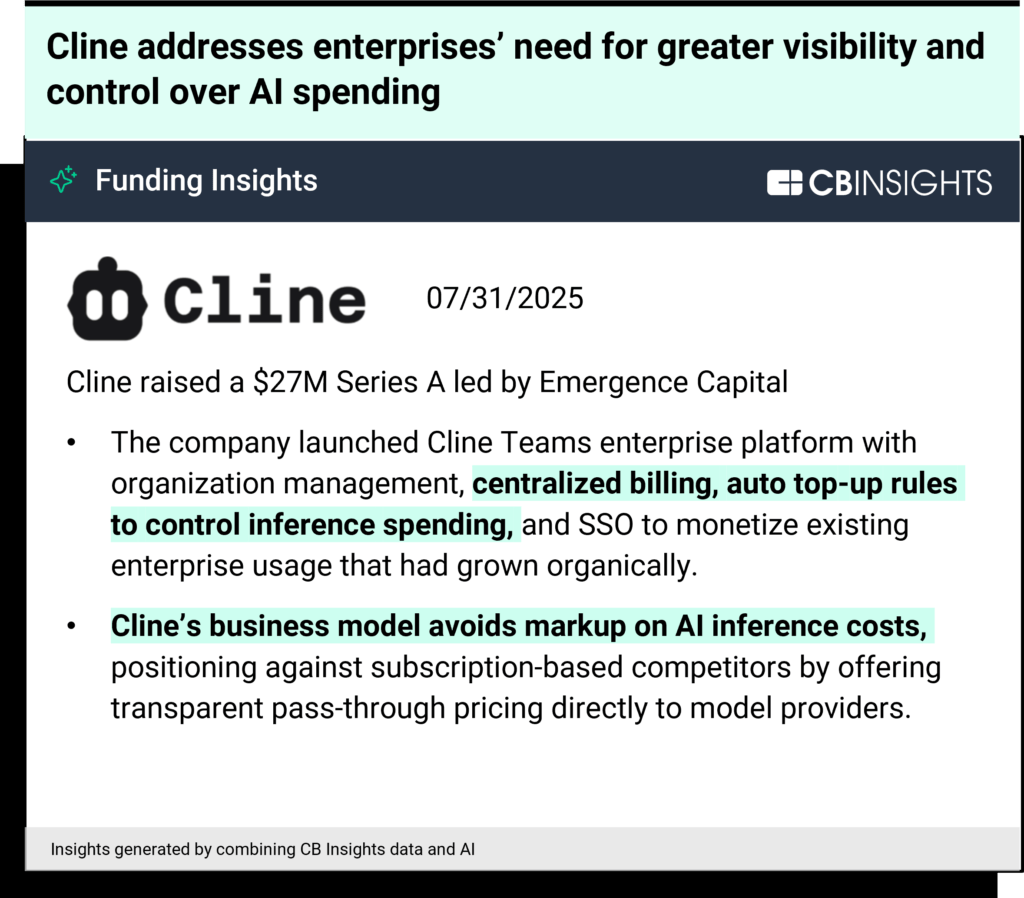
Cost management: At the end of the AI agent value chain, cost monitoring & productivity measurement will become more important as agents operate autonomously. For example, a16z-backed Larridin aims to give organizations visibility into AI spend and tool effectiveness. Other companies like coding AI agent Cline are building cost control solutions directly into their platforms to manage AI inference expenses.
Source: CB Insights Deal Agent
Click into each market to view the full description and market players on the CB Insights platform.
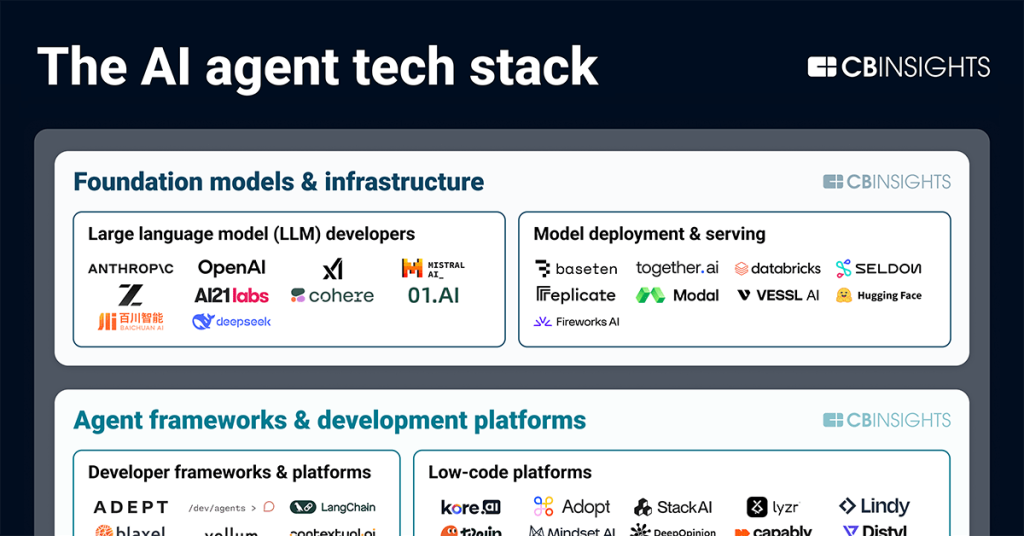
Foundation models & infrastructure
Large language models (LLMs) form the cognitive core of AI agents. This layer also covers the compute, hosting, and inference systems required to serve models at scale.
Agent frameworks & development platforms
Companies in this layer provide the software frameworks, SDKs, and low-code environments used to design, build, and deploy AI agents across different modalities and use cases.
Tool integration
AI agents leverage “tools” to interact with external systems and perform real-world actions, such as browsing the web. This includes Model Context Protocol (MCP) implementations that standardize how agents connect to data sources and tools.
Context
This layer supplies agents with structured data, embeddings, and memory systems so they can retain, retrieve, and apply relevant information over time.
Orchestration
This is the coordination layer that manages complex workflows involving multiple AI agents or models.
Oversight
Companies here target authentication, security, monitoring, and governance functions that ensure agent actions remain safe, compliant, and aligned with intended outcomes.
If you aren’t already a client, sign up for a free trial to learn more about our platform.