You’re not short on tools. Or models. Or frameworks.
What you’re short on is a principled way to use them — at scale.
Building effective generative AI workflows, especially agentic ones, means navigating a combinatorial explosion of choices.
Every new retriever, prompt strategy, text splitter, embedding model, or synthesizing LLM multiplies the space of possible workflows, resulting in a search space with over 10²³ possible configurations.
Trial-and-error doesn’t scale. And model-level benchmarks don’t reflect how components behave when stitched into full systems.
That’s why we built syftr — an open source framework for automatically identifying Pareto-optimal workflows across accuracy, cost, and latency constraints.
The complexity behind generative AI workflows
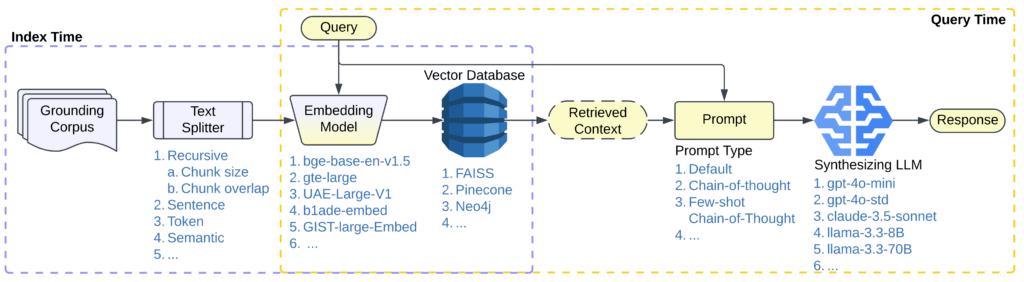
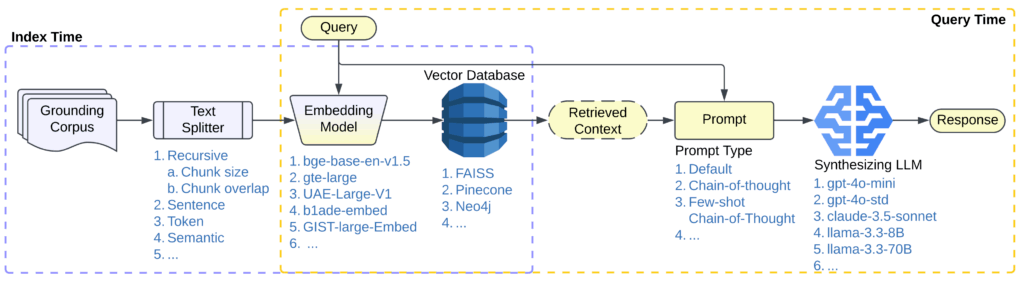
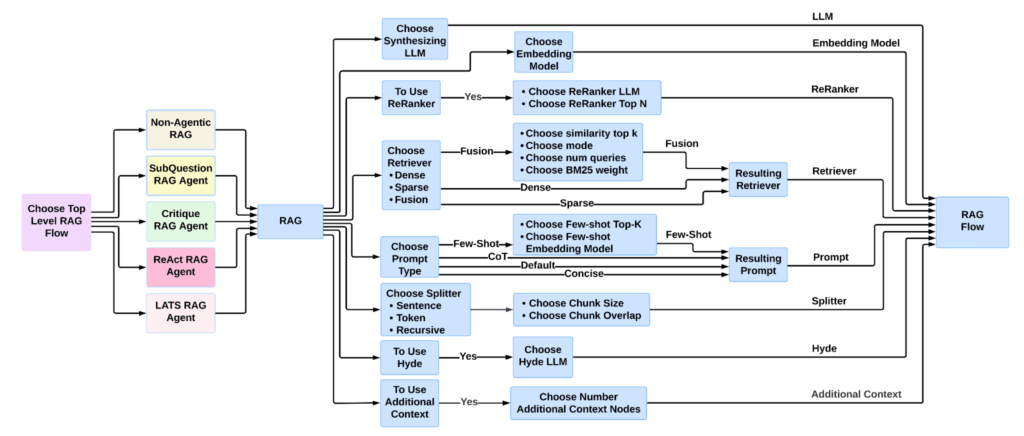
To illustrate how quickly complexity compounds, consider even a relatively simple RAG pipeline like the one shown in Figure 1.
Each component—retriever, prompt strategy, embedding model, text splitter, synthesizing LLM—requires careful selection and tuning. And beyond those decisions, there’s an expanding landscape of end-to-end workflow strategies, from single-agent workflows like ReAct and LATS to multi-agent workflows like CaptainAgent and Magentic-One.
What’s missing is a scalable, principled way to explore this configuration space.
That’s where syftr comes in.
Its open source framework uses multi-objective Bayesian Optimization to efficiently search for Pareto-optimal RAG workflows, balancing cost, accuracy, and latency across configurations that would be impossible to test manually.
Benchmarking Pareto-optimal workflows with syftr
Once syftr is applied to a workflow configuration space, it surfaces candidate pipelines that achieve strong tradeoffs across key performance metrics.
The example below shows syftr’s output on the CRAG (Comprehensive RAG) Sports benchmark, highlighting workflows that maintain high accuracy while significantly reducing cost.
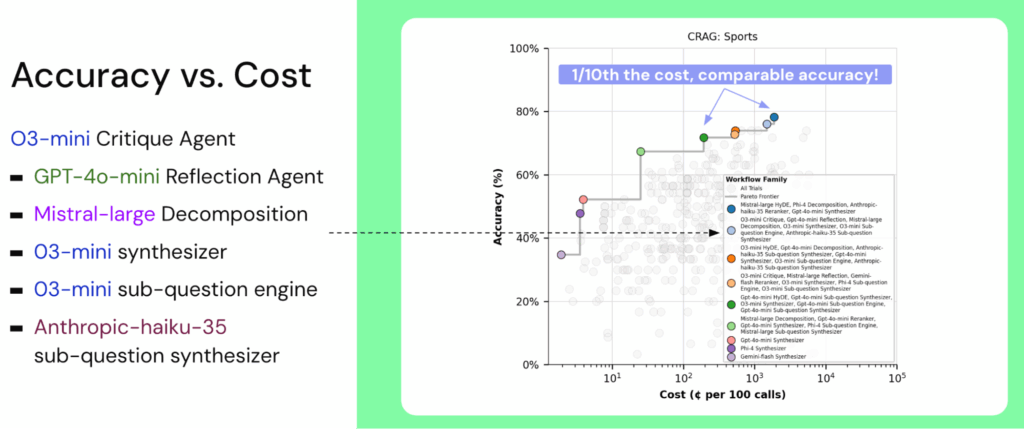
While Figure 2 shows what syftr can deliver, it’s equally important to understand how those results are achieved.
At the core of syftr is a multi-objective search process designed to efficiently navigate vast workflow configuration spaces. The framework prioritizes both performance and computational efficiency – essential requirements for real-world experimentation at scale.
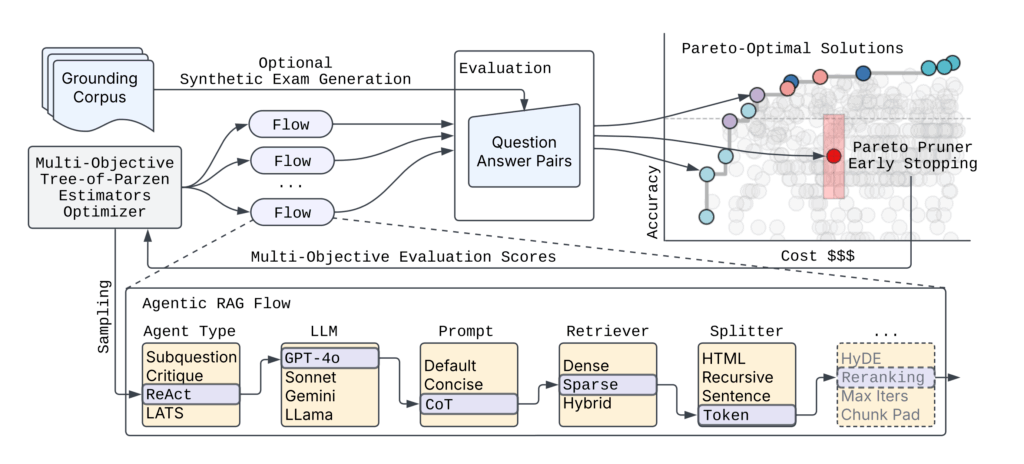
Since evaluating every workflow in this space isn’t feasible, we typically evaluate around 500 workflows per run.
To make this process even more efficient, syftr includes a novel early stopping mechanism — Pareto Pruner — which halts evaluation of workflows that are unlikely to improve the Pareto frontier. This significantly reduces computational cost and search time while preserving result quality.
Why current benchmarks aren’t enough
While model benchmarks, like MMLU, LiveBench, Chatbot Arena, and the Berkeley Function-Calling Leaderboard, have advanced our understanding of isolated model capabilities, foundation models rarely operate alone in real-world production environments.
Instead, they’re typically one component — albeit an essential one — within larger, sophisticated AI systems.
Measuring intrinsic model performance is critical, but it leaves open critical system-level questions:
How do you construct a workflow that meets task-specific goals for accuracy, latency, and cost?
Which models should you use—and in which parts of the pipeline?
syftr addresses this gap by enabling automated, multi-objective evaluation across entire workflows.
It captures nuanced tradeoffs that emerge only when components interact within a broader pipeline, and systematically explores configuration spaces that are otherwise impractical to evaluate manually.
syftr is the first open-source framework specifically designed to automatically identify Pareto-optimal generative AI workflows that balance multiple competing objectives simultaneously — not just accuracy, but latency and cost as well.
It draws inspiration from existing research, including:
AutoRAG, which focuses solely on optimizing for accuracy
Kapoor et al. ‘s work, AI Agents That Matter, which emphasizes cost-controlled evaluation to prevent incentivizing overly costly, leaderboard-focused agents. This principle serves as one of our core research inspirations.
Importantly, syftr is also orthogonal to LLM-as-optimizer frameworks like Trace and TextGrad, and generic flow optimizers like DSPy. Such frameworks can be combined with syftr to further optimize prompts in workflows.
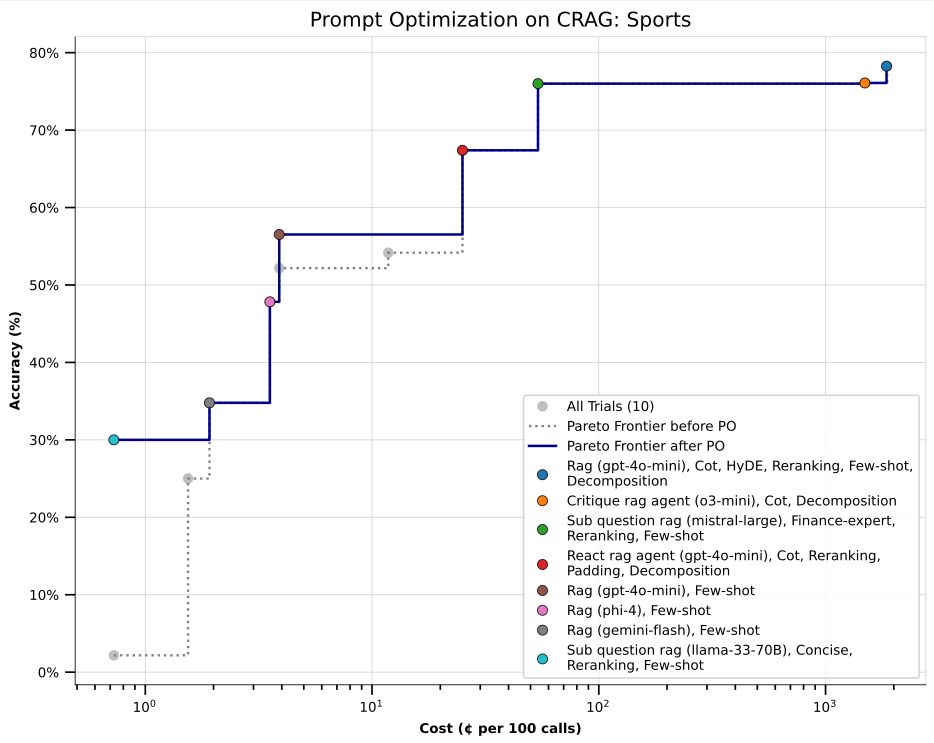
In early experiments, syftr first identified Pareto-optimal workflows on the CRAG Sports benchmark.
We then applied Trace to optimize prompts across all of those configurations — taking a two-stage approach: multi-objective workflow search followed by fine-grained prompt tuning.
The result: notable accuracy improvements, especially in low-cost workflows that initially exhibited lower accuracy (those clustered in the lower-left of the Pareto frontier). These gains suggest that post-hoc prompt optimization can meaningfully boost performance, even in highly cost-constrained settings.
This two-stage approach — first multi-objective configuration search, then prompt refinement — highlights the benefits of combining syftr with specialized downstream tools, enabling modular and flexible workflow optimization strategies.
Building and extending syftr’s search space
Syftr cleanly separates the workflow search space from the underlying optimization algorithm. This modular design enables users to easily extend or customize the space, adding or removing flows, models, and components by editing configuration files.
The default implementation uses Multi-Objective Tree-of-Parzen-Estimators (MOTPE), but syftr supports swapping in other optimization strategies.
Contributions of new flows, modules, or algorithms are welcomed via pull request at github.com/datarobot/syftr.
Built on the shoulders of open source
syftr builds on a number of powerful open source libraries and frameworks:
Ray for distributing and scaling search over large clusters of CPUs and GPUs
Ray Serve for autoscaling model hosting
Optuna for its flexible define-by-run interface (similar to PyTorch’s eager execution) and support for state-of-the-art multi-objective optimization algorithms
LlamaIndex for building sophisticated agentic and non-agentic RAG workflows
HuggingFace Datasets for fast, collaborative, and uniform dataset interface
Trace for optimizing textual components within workflows, such as prompts
syftr is framework-agnostic: workflows can be constructed using any orchestration library or modeling stack. This flexibility allows users to extend or adapt syftr to fit a wide variety of tooling preferences.
Case study: syftr on CRAG Sports
Benchmark setup
The CRAG benchmark dataset was introduced by Meta for the KDD Cup 2024 and includes three tasks:
Task 1: Retrieval summarization
Task 2: Knowledge graph and web retrieval
Task 3: End-to-end RAG
syftr was evaluated on Task 3 (CRAG3), which includes 4,400 QA pairs spanning a wide range of topics. The official benchmark performs RAG over 50 webpages retrieved for each question.
To increase difficulty, we combined all webpages across all questions into a single corpus, creating a more realistic, challenging retrieval setting.
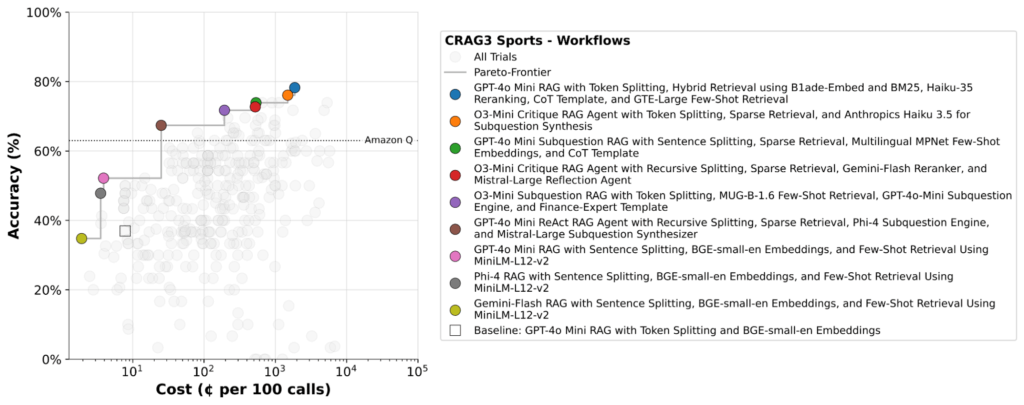
Note: Amazon Q pricing uses a per-user/month pricing model, which differs from the per-query token-based cost estimates used for syftr workflows.
Key observations and insights
Across datasets, syftr consistently surfaces meaningful optimization patterns:
Non-agentic workflows dominate the Pareto frontier. They’re faster and cheaper, leading the optimizer to favor these configurations more frequently than agentic ones.
GPT-4o-mini frequently appears in Pareto-optimal flows, suggesting it offers a strong balance of quality and cost as a synthesizing LLM.
Reasoning models like o3-mini perform well on quantitative tasks (e.g., FinanceBench, InfiniteBench), likely due to their multi-hop reasoning capabilities.
Pareto frontiers eventually flatten after an initial rise, with diminishing returns in accuracy relative to steep cost increases, underscoring the need for tools like syftr that help pinpoint efficient operating points.
We routinely find that the workflow at the knee point of the Pareto frontier loses just a few percentage points in accuracy compared to the most accurate setup — while being 10x cheaper.
syftr makes it easy to find that sweet spot.
Cost of running syftr
In our experiments, we allocated a budget of ~500 workflow evaluations per task. Although exact costs vary based on the dataset and search space complexity, we consistently identified strong Pareto frontiers with a one-time search cost of approximately $500 per use case.
We expect this cost to decrease as more efficient search algorithms and space definitions are developed.
Importantly, this initial investment is minimal relative to the long-term gains from deploying optimized workflows, whether through reduced compute usage, improved accuracy, or better user experience in high-traffic systems.
For detailed results across six benchmark tasks, including datasets beyond CRAG, refer to the full syftr paper.
Getting started and contributing
To get started with syftr, clone or fork the repository on GitHub. Benchmark datasets are available on HuggingFace, and syftr also supports user-defined datasets for custom experimentation.
The current search space includes:
9 proprietary LLMs
11 embedding models
4 general prompt strategies
3 retrievers
4 text splitters (with parameter configurations)
4 agentic RAG flows and 1 non-agentic RAG flow, each with associated hierarchical hyperparameters
New components, such as models, flows, or search modules, can be added or modified via configuration files. Detailed walkthroughs are available to support customization.
syftr is developed fully in the open. We welcome contributions via pull requests, feature proposals, and benchmark reports. We’re particularly interested in ideas that advance the research direction or improve the framework’s extensibility.
What’s ahead for syftr
syftr is still evolving, with several active areas of research designed to extend its capabilities and practical impact:
Meta-learning
Currently, each search is performed from scratch. We’re exploring meta-learning techniques that leverage prior runs across similar tasks to accelerate and guide future searches.
Multi-agent workflow evaluation
While multi-agent systems are gaining traction, they introduce additional complexity and cost. We’re investigating how these workflows compare to single-agent and non-agentic pipelines, and when their tradeoffs are justified.
Composability with prompt optimization frameworks
syftr is complementary to tools like DSPy, Trace, and TextGrad, which optimize textual components within workflows. We’re exploring ways to more deeply integrate these systems to jointly optimize structure and language.
More agentic tasks
We started with question-answer tasks, a critical production use case for agents. Next, we plan to rapidly expand syftr’s task repertoire to code generation, data analysis, and interpretation. We also invite the community to suggest additional tasks for syftr to prioritize.
As these efforts progress, we aim to expand syftr’s value as a research tool, a benchmarking framework, and a practical assistant for system-level generative AI design.
If you’re working in this space, we welcome your feedback, ideas, and contributions.
Try the code, read the research
To explore syftr further, check out the GitHub repository or read the full paper on ArXiv for details on methodology and results.
Syftr has been accepted to appear at the International Conference on Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) in September, 2025 in New York City.
We look forward to seeing what you build and discovering what’s next, together.