There is now growing evidence to suggest that more people are turning to AI chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, instead of Google Search, to find information online.
Since its launch in 2022, ChatGPT has handled over 365 billion search queries every year at a growth rate that is 5.5 times faster than Google Search, which took 11 years to reach the same milestone. These figures were revealed in a recent report on AI trends published by prominent investor and analyst Mary Meeker.
Widely known as the ‘Queen of the Internet’, Meeker boasts of a strong track record in correctly identifying major disruptions in the tech industry such as the rise of social media platforms like Facebook, smartphone adoption, etc.
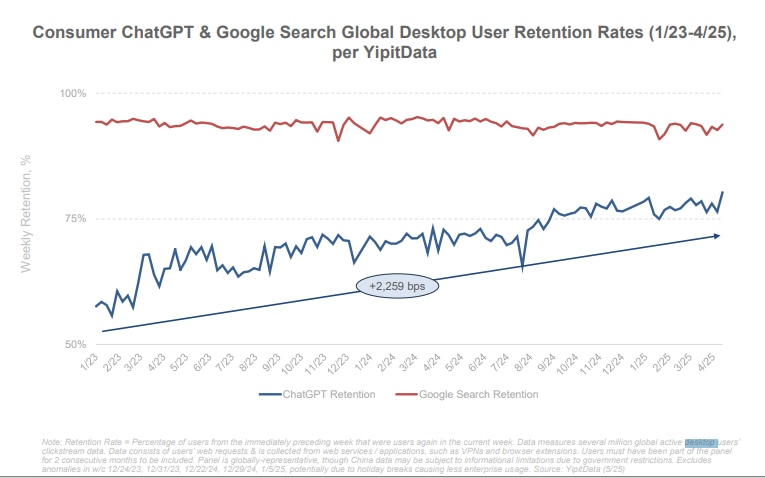 ChatGPT is catching up in user retention, though it still trails Google Search in absolute percentage. (Image credit: Bond VC)
ChatGPT is catching up in user retention, though it still trails Google Search in absolute percentage. (Image credit: Bond VC)
Her first report in six years, the 360-page analysis explores the state of AI and its impact on global behaviour, industries, and economic systems. “We’ve never seen anything like the user growth of ChatGPT, particularly outside the US, and it shows how the global dynamics of tech and distribution have changed,” Meeker was quoted as saying by Axios.
These figures point to a potential mass deflection away from traditional search engines towards AI chatbots like ChatGPT. It comes weeks after Eddy Cue, a senior executive at Apple, testified in the Google antitrust remedies trial that search volume to its Safari browser (which runs on Google’s search engine) had declined for the first time in 22 years. Cue’s testimony managed to spook Google parent Alphabet’s investors, sending shares down 7.5 per cent.

Google is also battling a major antitrust challenge in the US, with the Department of Justice (DOJ) eyeing a potential breakup of its core search and advertising businesses. AI featured prominently in the antitrust remedies trial against Google, where the DOJ essentially argued that AI was just another way for Google to extend its illegal search monopoly.
On the other hand, Google has suggested that AI is making the online search market more competitive in order to defend itself from the monopoly claims.
Story continues below this ad
Can ChatGPT replace Google Search?
While AI tools have seen rapid growth, the Meeker report pointed out that data and internet access may be key differentiating factors in the journeys of OpenAI and Google. When Google was founded in 1998, it sought to ‘organise the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful’ at a time when internet access was just emerging and smartphones did not exist.
Today, AI companies are able to leverage vast amounts of data that have already been digitised and made accessible for use. “AI is a compounder – on internet infrastructure, which allows for wicked-fast adoption of easy-to-use broad-interest services,” the report noted.
“Thanks to the rise in low-cost satellite-driven Internet connectivity / access, the potential for the 2.6B (or 32% of the world’s population) that is not online to come online is increasing. These new users will start from scratch with AI functionality,” the report added.
Based on data from Morgan Stanley, the report also speculated that while it took between 6-12 years for 50 per cent households in the US to have access to mobile and desktop internet, it will take only 3 years for the same number of households to become users of AI platforms.
Story continues below this ad
But even if it seems like more users are opting for AI chatbots and AI-powered search engines, traditional search engines might still have the upper hand (for now). A study published by SEO consultancy firm OneLittleWeb in May 2025, found that the total number of visits to the top 10 AI chatbots in 2024 was only 2.96 per cent of search engine traffic.
Regardless, Google is not exactly sitting on the sidelines. If anything, the tech giant has doubled down on using AI to augment its search functions with AI Mode and AI Overviews in Google Search.
Other findings of the report
The report identified India as a key user-base market for AI companies, owing to its large demography and internet penetration. It is the second largest market for ChatGPT, and contributes the highest percentage of its mobile app users (13.5 per cent), ahead of countries like the US (8.9 per cent), and Germany (3 per cent).
It also highlighted the unprecedented pace at which AI adoption is rising. For instance, it took the likes of Instagram, WhatsApp, and YouTube between 2-4 years to reach 100 million users, but for ChatGPT, it took less than 3 months.
Story continues below this ad
In addition, the report provided inputs on the battle between open and closed AI models. While closed models such as OpenAI’s GPT-4 or Anthropic’s Claude follow a centralised, capital-intensive arc, startups, academics, and governments without billion-dollar budgets have access to frontier AI models such as Meta’s Llama or Mistral’s Mixtral as they can easily be downloaded from platforms like Hugging Face.
“The split has consequences. Open-source is fueling sovereign AI initiatives, local language models, and community-led innovation. Closed models, meanwhile, are dominating consumer market share and large enterprise adoption. We’re watching two philosophies unfold in parallel – freedom vs. control, speed vs. safety, openness vs. optimization – each shaping not just how AI works, but who gets to wield it,” the report said.
“And China (as of Q2:25) – based on the number of large-scale AI models released – is leading the open-source race, with three large-scale models released in 2025 – DeepSeek-R1, Alibaba Qwen-32B and Baidu Ernie 4.5,” it added.


