Large multimodal models excel in multimodal tasks but face significant
computational challenges due to excessive computation on visual tokens. Unlike
token reduction methods that focus on token-level redundancy, we identify and
study the computation-level redundancy on vision tokens to ensure no
information loss. Our key insight is that vision tokens from the pretrained
vision encoder do not necessarily require all the heavy operations (e.g.,
self-attention, FFNs) in decoder-only LMMs and could be processed more lightly
with proper designs. We designed a series of experiments to discover and
progressively squeeze out the vision-related computation redundancy. Based on
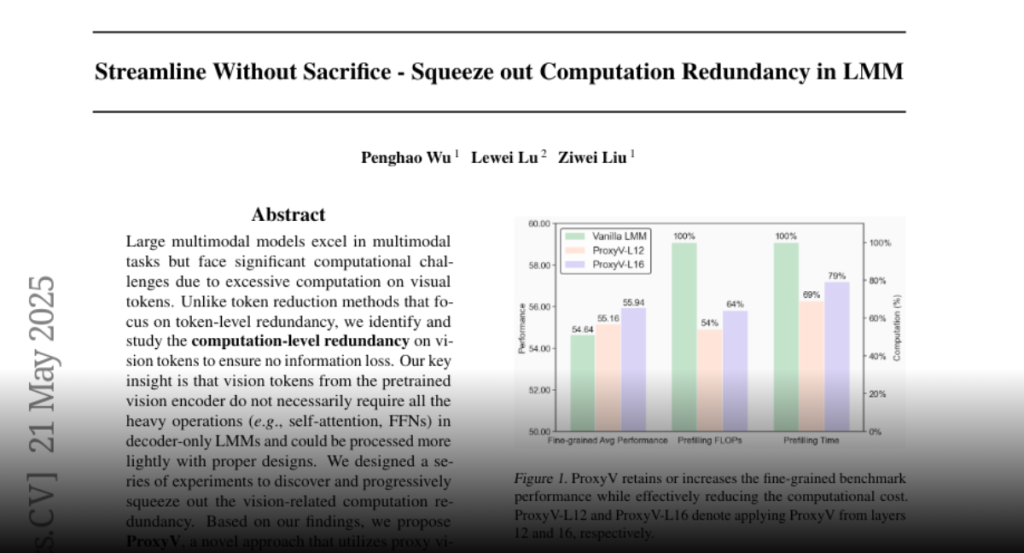
our findings, we propose ProxyV, a novel approach that utilizes proxy vision
tokens to alleviate the computational burden on original vision tokens. ProxyV
enhances efficiency without compromising performance and can even yield notable
performance gains in scenarios with more moderate efficiency improvements.
Furthermore, the flexibility of ProxyV is demonstrated through its combination
with token reduction methods to boost efficiency further. The code will be made
public at this https://github.com/penghao-wu/ProxyV URL.

1 Comment
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.