CB Insights is launching the 9th annual AI 100 — a ranking of the world’s top emerging AI companies. From observability to infrastructure security to vertical AI agents, this year’s winners are shaping the future of intelligent systems across industries.
The AI space is evolving at an unprecedented rate. Since the start of 2024, thousands of new AI companies have formed, and funding to AI companies has surpassed $170B, primarily driven by titans like OpenAI and Anthropic.
Given this momentum, the ecosystem is larger and more challenging to navigate than ever.
Our annual AI 100 list is designed to cut through this noise and highlight the next wave of AI winners, with a focus on early-stage players that are showing strength in terms of market traction, investor quality, and talent.
Leveraging CB Insights datasets such as deal activity, industry partnerships, team strength, investor strength, patent activity, and our proprietary Mosaic Scores, we selected 100 winners out of a cohort of 17K+ companies. We also analyzed CB Insights’ exclusive interviews with software buyers and dug into Analyst Briefings submitted directly to us by startups.
Below, we map out the winners, categorizing them based on their core offering. Key trends and category definitions follow.
Please click to enlarge. Data as of 4/23/25.
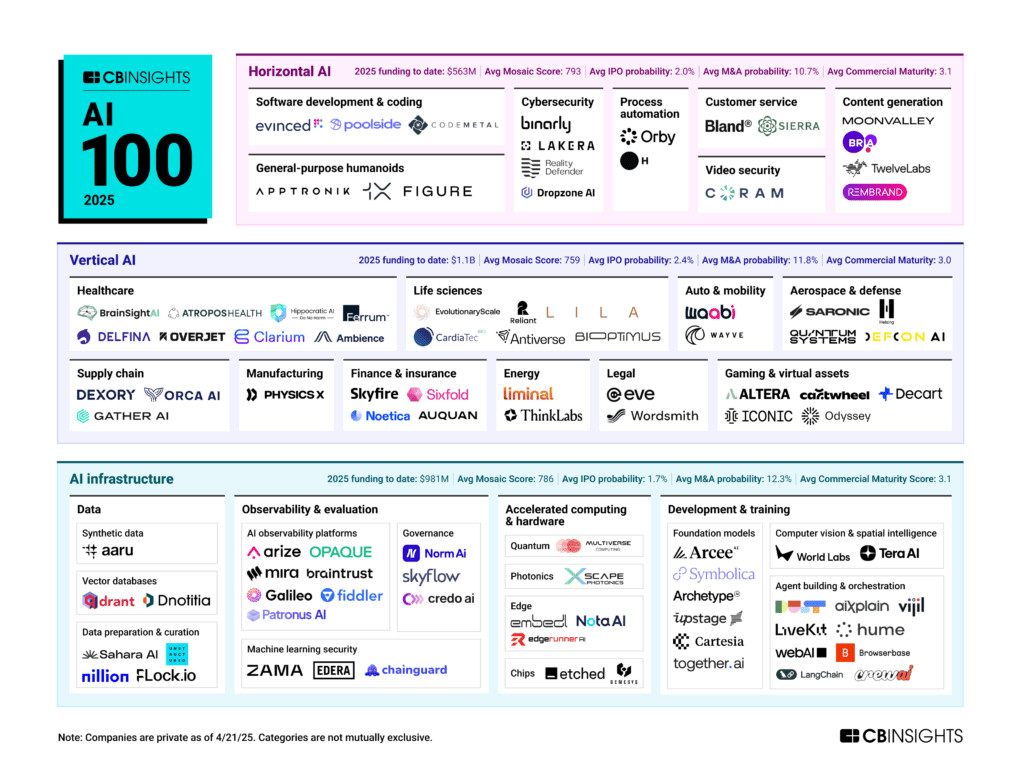
![]() CBI customers: Get data on the winners
CBI customers: Get data on the winners
Key takeaways on the AI 100
AI agents dominate the conversation. These applications, which automate tasks and processes for human users, are the next wave of genAI. Having made their way into virtually every horizontal and enterprise function, AI agents are also coming for infrastructure and verticalized applications. AI agents and supporting infrastructure make up 21% of this year’s companies, and the investors we spoke with consistently cited this space as a priority.
ML security has become table stakes. The need to secure AI applications has grown in lockstep with the proliferation of genAI and agentic AI. 46% of strategy team leaders point to security as the primary barrier to genAI adoption, according to a recent CB Insights survey. Machine learning security companies are hardening AI algorithms and foundational models like LLMs, while also defending against increasingly sophisticated AI-powered attacks.
AI observability and governance are critical gaps. Widespread use of AI is exposing the technology’s cracks — hallucinations, lack of orchestration, and output inaccuracies. It’s clear that AI ubiquity can’t exist without robust monitoring. Companies are rising to meet this need. Startups in this year’s list cover areas like observability and governance, while a small cohort also monitors AI agents to ensure reliability and compliance.
The future is physical. Looking ahead, AI will evolve beyond software AI agents to a physical state. Advances in disparate areas of AI development — including robotics, multimodal image and voice models, edge computing, synthetic data, and spatial intelligence — provide the scaffolding for physical AI, which pairs AI software with hardware to take action in physical environments. Industrial humanoids represent an early manifestation of this, while future permutations could include fully autonomous defense drones, home companion robots, and more.
Vertical applications are exploding. In 2024, the horizontal companies in this AI 100 cohort received more funding than their vertical and infrastructural counterparts — $1.6B compared to $1.2B each for infrastructure and vertical. But in 2025 so far, the funding picture looks very different: Vertical winners lead the way with $1.1B in funding raised.
Category breakdown
AI INFRASTRUCTURE
On the foundation model front, infrastructure newcomers are rapidly releasing models that rival industry leaders, signaling a maturing market where technical excellence and novel approaches increasingly compete with raw computing power. We identified winners across large language, edge, reasoning, small language, and multimodal models.
Meanwhile, as AI applications — particularly agents — become more autonomous and widespread, the need for robust monitoring, governance, and cybersecurity solutions has grown in lockstep.
We’ve heard this in our conversations with AI investors, as well. Mozilla Ventures, a lead investor in Credo AI, views governance as a strategic imperative. Mohamed Nanabhay, Managing Partner, notes:
“…We think that the AI governance sector itself will take on a crucial role of creating value for enterprises, allowing companies that leverage governance to deploy AI faster through the reduction of risk with a greater competitive advantage as a result.”
Category definitions:
DATA
Synthetic data: Artificially generated or altered information that mimics real-world data without privacy concerns. Aaru uses a multi-agent approach to create population simulations for predictive decision-making applications like consumer behavior and electoral modeling.
Data preparation & curation: Tools and platforms that clean, transform, label, and organize data to make it suitable for AI training and deployment, encompassing data cleaning and specialized data processing. Unstructured, for instance, helps organizations capture unstructured data from various documents and convert it into AI-friendly formats such as JSON to train LLMs.
Vector databases: Solutions that provide enterprises with an easy way to store, search, and index unstructured data at a speed, scale, and efficiency that current relational (and non-relational) databases cannot offer. For example, Qdrant provides an open-source vector database that allows developers to build production-ready applications that use nearest neighbor search functionality.
DEVELOPMENT & TRAINING
Foundation models: Pre-built AI algorithms and architectures that can be deployed, fine-tuned, or integrated into applications, spanning general-purpose foundation models and specialized domain-specific models. This category includes large language, edge, reasoning, small language, and multimodal AI models. For instance, Archetype AI‘s Newton model processes multimodal sensor data and natural language to provide insights and predictions about physical environments.
Agent building & orchestration: This category covers AI agent development platforms for building, orchestrating, and monitoring agents. Companies like LangChain provide a framework for building context-aware reasoning applications with tools for debugging, testing, and monitoring app performance across the entire application lifecycle.
Computer vision & spatial intelligence: Technology that enables AI systems to understand, interpret, and interact with physical spaces and 3D environments, including mapping, navigation, and spatial data processing capabilities. Notably, World Labs develops Large World Models (LWMs) that enable AI systems to perceive, generate, and interact with both virtual and real 3D environments using spatial intelligence.
OBSERVABILITY & EVALUATION
AI observability platforms: These platforms monitor, measure, and assess AI model performance, reliability, and outputs, including tools for testing, benchmarking, and continuous improvement of AI systems. For instance, Arize’s platform allows teams to monitor, diagnose, and improve the performance of AI models and applications in production through tools based on open-source standards that integrate with existing AI infrastructure.
Governance: Solutions that establish policies, processes, and controls for responsible AI development and deployment, covering risk management, compliance, ethical oversight, and transparency requirements. For example, Credo AI offers a platform that automates AI oversight, risk management, and regulatory compliance while providing AI auditing to ensure system integrity and fairness.
Machine learning security (MLSec): Technologies that protect AI systems from vulnerabilities, attacks, and data breaches, including techniques for securing model training, inference, and data pipelines. Solutions developed by companies like Zama enable computation on encrypted data, allowing for privacy-preserving machine learning across industries that require data privacy and security.
ACCELERATED COMPUTING & HARDWARE
Edge: Platforms that provide the infrastructure and models to operate AI on “edge” devices such as tablets, IoT, autonomous vehicles, or smartphones. For example, EdgeRunner AI constructs an ensemble of small, task-specific models that work together to solve complex problems locally on devices, ensuring data privacy and security for heavily regulated industries.
Photonics: Solutions that use light (photons) instead of electrons for data processing, with the potential to significantly increase computing speeds. Companies in this category provide memory, interconnects, and system architecture. Xscape Photonics develops bandwidth-efficient photonics solutions to support AI/ML infrastructure.
Quantum: Companies providing novel techniques like model compression and hardware to support quantum commercialization. Multiverse Computing provides AI model compression technology to enable quantum AI workloads and processing.
Chips: Traditional chips, in addition to chips to support new AI technologies. Etched develops chips designed specifically for transformer inference, capable of processing extensive data for applications such as real-time voice agents and content generation.
HORIZONTAL AI
This category includes industry-agnostic solutions across visual media, text, code, audio, and interfaces. These function-specific solutions address common business needs regardless of industry, offering specialized intelligence that complements both vertical applications and foundational infrastructure.
AI agents in particular are beginning to upend the way in which enterprises think about software. Decibel Partners, a lead investor in multi-agent platform Dropzone AI, sees a movement toward productizing agents as full systems. Jéssica Leão, a Partner at Decibel, articulates this vision further:
“…We’re going to see the software world change because, again, you’re selling agents almost as if you’re selling back-end software.”
Horizontal AI solutions are increasingly tailored to serve distinct business functions while remaining broadly deployable. Startups in this category are developing sophisticated AI systems that excel in capabilities like content generation, customer support, process automation, and software development — all of which can be applied across industries.
Category definitions:
Content generation: AI systems that create text, images, video, and other media forms — spanning automated content production and multimodal generation. For example, Moonvalley’s genAI video model helps filmmakers by enabling prompt adherence, motion generation, and physics simulation using cleaned, fully licensed data.
Customer service: AI agents that autonomously handle customer service tasks or augment human agents. Sierra‘s platform, for instance, provides intelligent agents for customer support that engage in personalized interactions and integrate with existing call center technologies.
Cybersecurity: AI-powered solutions that detect, prevent, and respond to digital threats, vulnerabilities, and attacks, covering network security, threat intelligence, and automated incident response. Companies like Binarly use AI to detect and remediate vulnerabilities in firmware and software supply chains.
General-purpose humanoids: AI systems embedded in robotic bodies that mimic human capabilities, enabling physical interaction through perception and manipulation. For example, Figure develops autonomous humanoid robots that combine human-like dexterity with AI to perform a variety of tasks across industries like manufacturing, logistics, warehousing, and retail.
Process automation: Intelligent systems that autonomously handle repetitive business workflows, increasing efficiency by eliminating manual tasks. Orby AI offers a platform that observes enterprise processes and generates executable automations — particularly for complex, data-heavy operations in industries like tech and finance.
Software development & coding: AI solutions that assist with software development, code generation, debugging, and programming tasks, including automated code completion tools. For instance, Poolside offers foundation models and APIs that can be fine-tuned using a company’s own codebase and documentation to support internal dev teams.
Video security: Technologies that enable real-time analysis of video feeds, supporting faster detection and response to security threats. Coram AI develops cloud-based security camera systems with features like real-time AI alerts and natural language video search, allowing businesses to monitor properties remotely without extensive hardware replacements.
VERTICAL AI
Vertical AI is on the rise, with this year’s vertical winners surpassing the other category winners to capture over $1B in combined funding in 2025 YTD. They span 10 industries that represent a convergence of high-value problems, rich data availability, and regulatory momentum.
Some of the VCs we spoke with see specialization as the way of the future. Lila Tretikov, Partner and Head of AI Strategy at New Enterprise Associates (a lead investor for Twelve Labs, World Labs, and Orby AI), told us:
“We believe that there is going to be specialization, even within the model layer. And there’s going to be innovation in this layer, especially as we look at verticalization for specific use cases.”
The most well-represented verticals on this year’s list are healthcare (8 companies) and life sciences (6 companies). The healthcare industry as a whole is seeing breakthrough applications across multiple AI modalities — from agentic AI systems that can augment clinical workflows, to advanced machine vision for medical imaging analysis, to AI-accelerated drug discovery platforms that dramatically reduce R&D timelines.
This year’s cohort also saw significant representation in gaming & virtual assets (5 companies), finance & insurance (4 winners), and aerospace & defense (4 winners).
Category definitions:
Aerospace & defense: AI solutions designed for aerospace engineering, aviation operations, military applications, and defense systems, including autonomous navigation and threat detection technologies. For instance, Quantum Systems creates eVTOL unmanned aerial systems that serve critical defense applications, most notably in Ukraine.
Auto & mobility: AI applications for autonomous vehicles, transportation optimization, fleet management, and mobility services. Companies like Wayve are developing AI systems that use LLMs to provide real-time natural language explanations of driving decisions, helping improve users’ confidence.
Energy: Platforms that optimize energy production, distribution, and sustainability, including battery intelligence and AI assistance for electric grids. For example, Liminal leverages ultrasound and machine learning inspection solutions to improve battery cell quality, cost-effectiveness, and safety while enabling confident scaling of production.
Finance & insurance: AI solutions for financial services, banking, investment, and insurance sectors, covering payments, risk assessment, and portfolio monitoring. Skyfire’s financial stack enables AI agents to perform transactions without credit cards or bank accounts, allowing businesses to monetize their products, services, and data through AI agents.
Gaming & virtual assets: AI technologies that enhance gaming experiences, virtual environments, digital asset management, and immersive entertainment, including content generation and NPC (non-player character) intelligence. Altera‘s platform creates digital human beings that can interact with users and perform tasks autonomously, bringing empathy and human-like traits to digital interactions.
Healthcare: AI applications focused on clinical care delivery, medical operations, and patient management, including tools for clinical documentation automation, medical imaging analysis, decision support systems, remote patient monitoring, and healthcare supply chain optimization. In the dental field, Overjet provides an AI platform that enhances clinical care through radiographic analysis and optimizes claims processing for providers and payers.
Life sciences: AI solutions for pharmaceutical research, drug discovery, protein engineering, biological data analysis, and therapeutic development, including platforms for multiomics analysis, antibody design, foundation models for biology, and scientific experiment automation. Lila Sciences has developed a platform that integrates AI with autonomous laboratories to design, conduct, observe, and redesign experiments for scientific discovery.
Legal: AI tools for legal research, document analysis, contract management, compliance, and legal workflow automation, including case management, due diligence, and contract review. AI-powered tools like Eve help law firms streamline the full case lifecycle from intake to litigation by automating case intake, drafting legal documents, and managing discovery processes.
Manufacturing: Technology that optimizes industrial processes like factory automation, using virtual development and simulation. PhysicsX applies machine learning to physics simulations that optimize design and engineering processes across industries including aerospace, medical devices, and electric vehicles.
Supply chain: AI solutions that enhance logistics and supply chain operations, including warehouse management and route optimization & visibility. Dexory combines stock-scanning robots with a digital twin platform to provide real-time inventory and warehouse analytics for logistics and supply chain operations.
For information on reprint rights or other inquiries, please contact reprints@cbinsights.com.
If you aren’t already a client, sign
up for a free trial to learn more about our platform.
